MAKING BUSINESS DECISION
THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
The process of making decisions plays a crucial role in communication and leadership for operational, managerial, and strategic projects.
THE SIX-STEP DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- Problem identification : Define the problem as clearly and precisely as possible.
- Data collection : Gather problem-related data, including who,what,where,when,why, and how. Be sure to gather facts, not rumors or opinions about the problem.
- Solution generation : Detail every solution possible, including ideas that seem farfetched.
- Solution test : Evaluate solutions in terms of feasibility (can it be completed?), suitability (is it a permanent or a temporary fix?), and acceptability (can all participants form a consensus?).
- Solution selection : Select the solution that best solves the problem and meets the needs of the business.
- Solution Implementation : If the solution solves the problem, then the decisions made were correct. If not, then the decision were incorrect and the process begins again.
DECISION-MAKING ESSENTIALS
- A few key concepts about organizational structure will help our discussion of MIS decision-making tools.
- The structure of a typical organization is similar to a pyramid, and the different levels require different types of information to assist in decision making, problem solving, and opportunity capturing.
Operational
- At the operational level, employees develop, control, and maintain core business activities required to run the day-to-day operations.
- Operational decisions are considered structured decisions, which arise in situations where established processes offer potential solutions.
Managerial
- Emloyees are continuously evaluating company operations to hone the firm's abilities to identify, adapt to, and leverage change.
- these types of decision are considered semistructured decisions-occur in situations in which a few established processes help to evaluate potential solutions, but not enough to lead to a definite recommended decision.
Strategic
- Managers develop overall business strategies, goals, and objectives as part of the company's strategic plan.
- strategic decisions are highly unstructured decisions- occuring in situations which no procedures or rules exist to guide decision makers toward the correct choices.
ENHANCING DECISION MAKING WITH MIS
- A model is a simplified representation or abstraction of reality.
OPERATIONAL SUPPORT SYSTEMS
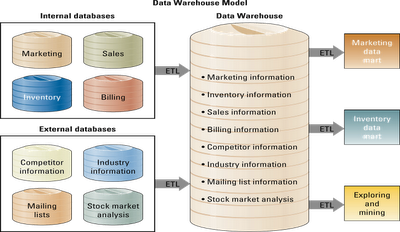
- Transactional information encompasses all the information contained within a single business process or unit of work.
- Its primary purpose is to support the performance of daily operational or structured decisions.
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is the capture of transaction and event information using technology to:
- process the information according to defined business rules.
- store the information.
- update existing information to reflect the new information.
A transaction processing system (TPS) is the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) and assists in making structured decisions.
MANAGERIAL SUPPORT SYSTEMS
Analytical information encompasses all organizational information.Its primary purpose is to support the performance of managerial analysis or semistructured decisions. Analytical information includes transactional information along with other information such as market and industry information.
Online analytical processing (OLAP) is the manipulation of information to create business intelligence in support of strategic decision making.
Decision support systems (DSSs)
- model information using OLAP, which provides assistance in evaluating and choosing among different courses of action.
- DSSs enable high-level managers to examine and manipulate large amounts of detailed data from different internal and external sources.
What-if analysis
What-if analysis checks the impact of a change in a variable or assumption on the model.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis, a special case of what-if analysis, is the study of the impact on other variables when one variable is changed repeatedly.
Goal-Seeking analysis
Goal-seeking analysis finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output.
Optimization analysis
Optimization analysis, an extension of goal-seeking analysis, finds the optimum value for a target variable by repeatedly changing other variables, subject to specified constraints.
By changing revenue and cost variables in an optimization analysis, managers can calculate the highest potential profits.
Constraints on revenue and cost variables can be taken into consideration, such as limits on the amount of raw materials the company can afford to purchase and limits on employees available to meet production needs.
STRATEGIC SUPPORT SYSTEMS
An executive information system (EIS) is a specialized DSS that supports senior-level executives and unstructured, long-term, nonroutine decisions requiring judgment, evaluation, and insight.
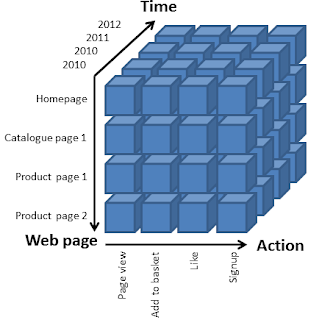
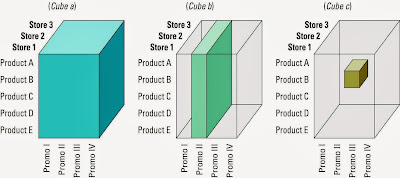
Glanularity refers to the level of detail