DATA WAREHOUSE FUNDAMENTALS
A Data Warehouse -> a logical collection of information-gathered from many different operational data bases-that supports business analysis activities and decision-making task.
Primary Purpose : to aggregate information throughout an organization into a single repository in such a way that employees can make decisions and undertake business analysis activities.
Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL) :
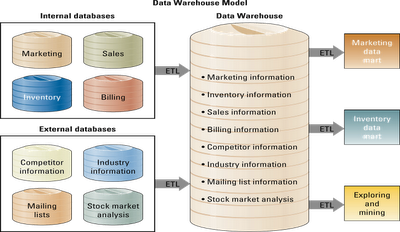
- is a process that extracts information from internal and external databases, transforms the information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the information into a data warehouse.
- the data warehouse then sends subsets of the information to data marts.
A DATA MART
= contains a subset of data warehouse information.
=to distinguish between data warehouses and data marts, think of data warehouse data as having more organizational focus and data marts as having focused information subsets particular to the needs of a given business unit.
=such as finance or production and operations.
DATA WAREHOUSE MODEL





MULTIDIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND DATA MINING
- Relational databases contains information a series of two - dimensional tables
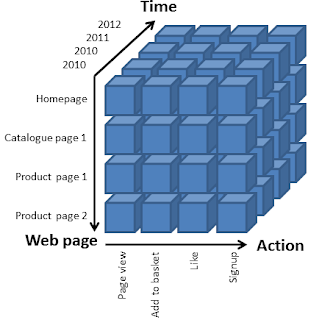
- In a data warehouse and data mart, information is a multidimensional, it contains layers of columns and rows
- Dimension- a particular attribute of information

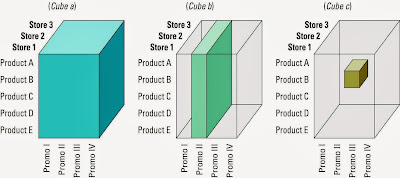
Cube
= Common term for the representation of multidimensional information.

Data Mining
= is the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone.
Data-mining tools
= use a variety of techniques to
find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information and infer rules from them that predict future behavior and guide decision making.
INFORMATION CLEANSING OR SCRUBBING
= is a process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information.
CONTACT INFORMATION IN OPERATIONAL SYSTEMS

STANDARDIZING CUSTOMER NAME FROM OPERATIONAL SYSTEMS

INFORMATION CLEANSING ACTIVITIES

ACCURATE AND COMPLETE INFORMATION

BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
- refers to applications and technologies that are used to gather, provide access to, and analyze data and information to support decision-making efforts.
ENABLING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
1. TECHNOLOGY
= the largest companies today can create enterprisewide BI systems that compute and monitor metrics on virtually every variable important for managing the company.
2. PEOPLE
= Organizations can improve their decision making by having the right people making the decisions.
3. CULTURE
= A key responsibility of executives is to shape and manage corporate culture.
No comments:
Post a Comment